Share this
Silicon Valley Bank Collapse Driven by Social Media Panic
by Henry Chapman on March 31, 2023
Infegy social intelligence bears witness to the real time collapse of a financial institution
Silicon Valley Bank (SVB), a regional bank that has historically financed and served startup companies, suffered a catastrophic collapse due to several ill-advised risk management decisions, leading to a contemporary bank run. The ensuing panic among venture capitalists was evident in their alarmed tweets, expressing concerns about potentially losing billions of dollars held at SVB. In this brief, we provide an overview of how the crisis unfolded on social media platforms and discuss the government interventions implemented in response and the public reactions to those measures.
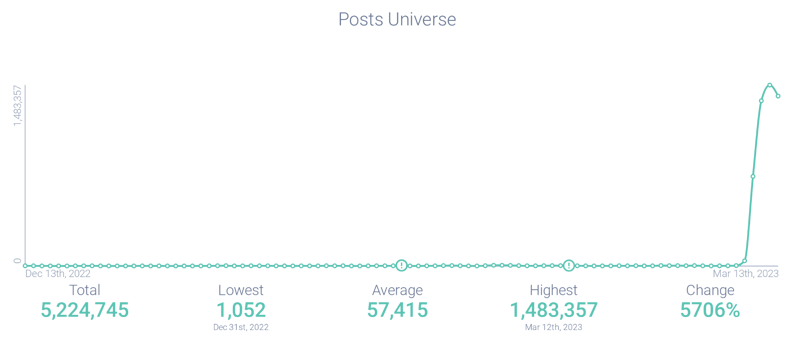
Figure 1: Post volume shows very little Silicon Valley Bank activity until a surge started on March 9, 2023; Infegy Atlas data.
Reasons why Silicon Valley Bank collapsed
Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) essentially collapsed because it could not meet its withdrawal obligations when thousands of its clients tried to pull their money simultaneously.
Back in 2022, SVB invested a large amount in US treasuries. However, these treasuries lost significant value as the US Federal Reserve rapidly raised interest rates. 2022 also saw a drop in growth and fundraising for tech startups – the bank's primary customer base – which led to increased withdrawals. This forced SVB to sell the previously mentioned treasuries at a loss.
The panic began when SVB went public with the need to sell a large portion of the company to cover these losses and meet the withdrawal demands. This news spread amongst a group of closely-connected tech venture capitalists, and then hit social media. This social media-propagated panic prompted a traditional bank run.
The FDIC eventually had to intervene, taking over the bank to restore order.
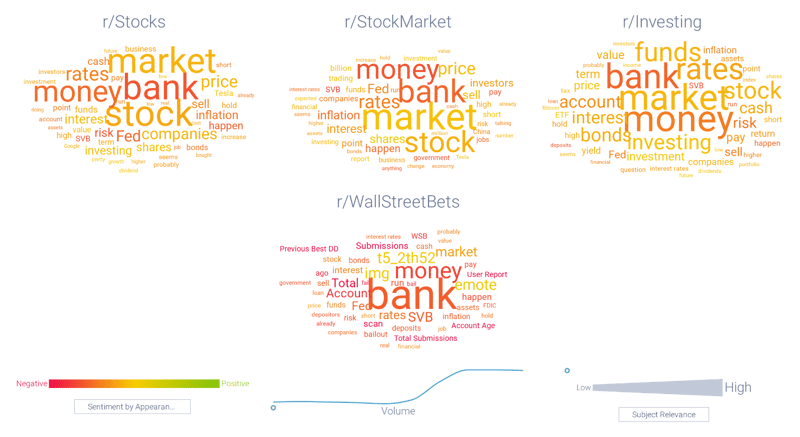
Figure 2: Word clouds showing how SVB conversation dominated the discussion across leading Finance subreddits; Infegy Atlas data.
Changing sentiment in the conversation
Before the collapse, there was minimal online conversation about SVB. However, on March 9, 2023, negative sentiment surrounding the bank began to simmer as discussions about bank runs and financial panic increased. Negative sentiment then exploded on March 10th.
This negativity starkly contrasted with the bank's previously positive reputation as a well-liked institution that supported the startup industry for 40 years. For many years, SVB was the go-to bank for a startup and their needed financial services.
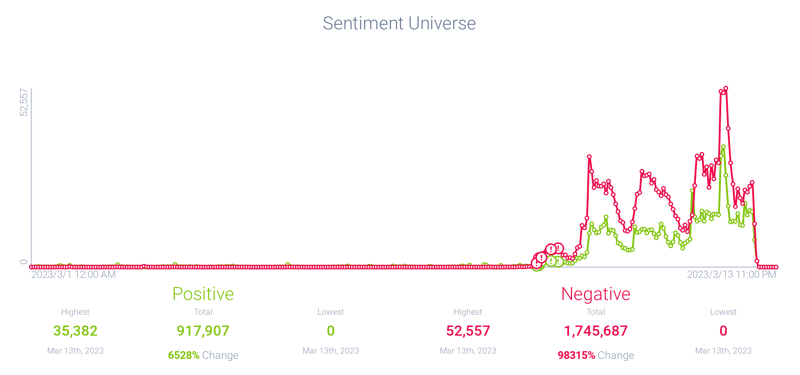
Figure 3: Negative sentiment surges around Silicon Valley Bank; Infegy Atlas data.
Changing themes in the conversation
Infegy Atlas Themes, an analytic capability within the Infegy Atlas platform, provides a more granular understanding of the crisis.
All over social media, venture capitalists and other financial experts began sharing news of SVB’s instability, using warning signs and messaging that indicated their panic. Conversations involving the Infegy Atlas Theme - Risk peaked on March 9, 2023.
Hours later, on March 10, 2023, the Infegy Atlas Theme Intent > Churn theme began to surge: this reflected investors' discussions as they attempted to withdraw their funds. However, after the FDIC's intervention halted withdrawals, Risk surged again as account holders realized they could not get their money back immediately.
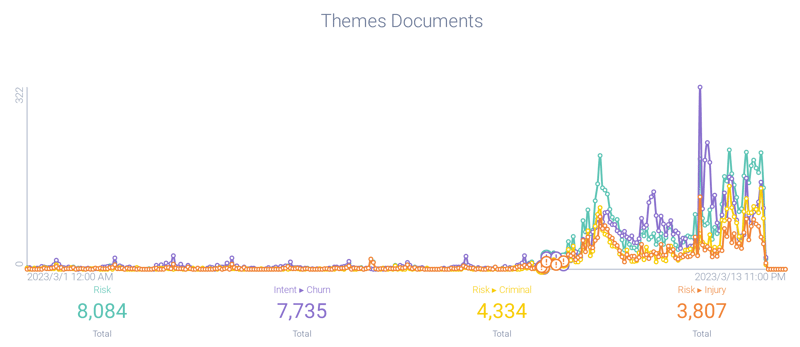
Figure 4: Theme analysis showing initial Risk conversation followed by a surge of Intent -> Churn; Infegy Atlas data.
Changing emotions in the conversation
On Monday morning, the US government stepped in and guaranteed that while shareholders would lose their entire investment, account holders in the bank would be made whole.
However, Infegy Emotions analysis shows that the dominant emotion expressed online about SVB and the government intervention was anger. Consumers were furious about what they perceived as a bailout by the Federal Reserve, fueled by lingering resentment from the 2008 Financial Crisis. Reddit users' sentiment towards Ben Bernanke, former chairman of the Federal Reserve, shows a positivity rate of only 25%, illustrating this frustration.
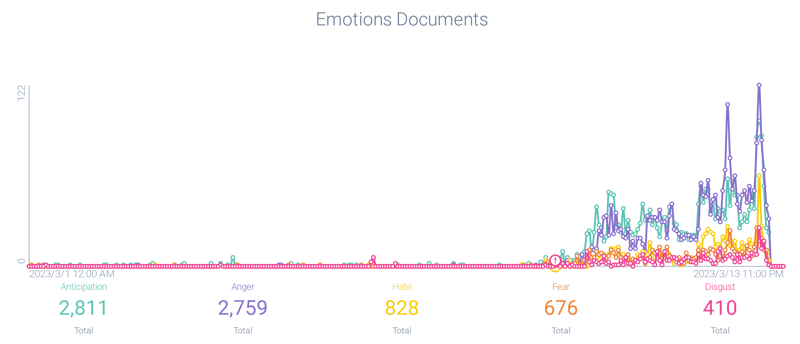
Figure 5a: Emotional analysis showing Anger as a predominant emotion; Infegy Atlas data.
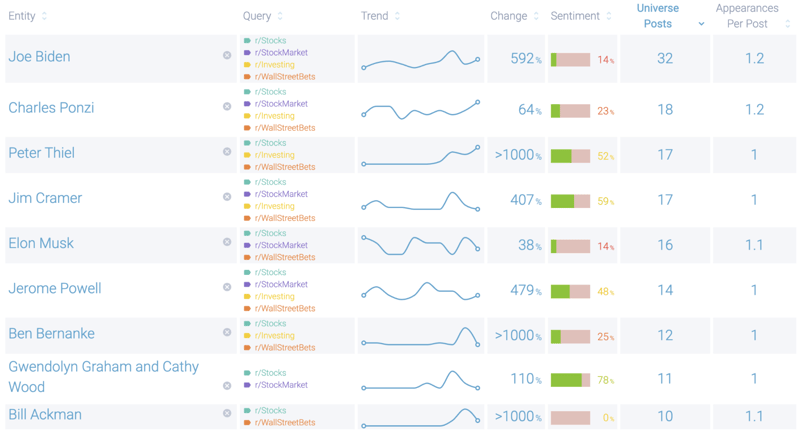
Figure 5b: Entity table showing negative sentiment around Ben Bernanke, the former chairman of the US Federal Reserve; Infegy Atlas data.
The importance of brand trustworthiness in a socially mediated world
The collapse of Silicon Valley Bank was a multifaceted event with far-reaching consequences. Social media became the vessel that carried the news of SVB’s troubles fast and far.
As news of the bank's collapse spread, online conversations shifted dramatically towards negative sentiment, and showed growing Themes of Risk, and customers’ intent to churn.
The crisis also revealed underlying anger among consumers regarding perceived bailouts and government intervention, as demonstrated by the backlash against figures like Ben Bernanke.
The SVB collapse is a stark reminder of the fragile nature of financial institutions and the importance of maintaining public trust, especially given how social media connects people and spreads news.
Silicon Valley Bank Collapse: Key Takeaways
Discover how the rapid spread of panic on social media led to the sudden collapse of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB). Learn about the key events, reactions, and factors contributing to this financial crisis.
Understanding the Collapse
SVB failed to meet withdrawal demands after poor risk management and significant investment losses, triggering a bank run. The FDIC's intervention came as a measure to stabilize the situation.
Social Media's Role
Venture capitalists' alarmed tweets sparked panic, illustrating how social media can quickly escalate financial crises. Conversations about SVB surged on March 9, 2023, with increasing negative sentiment.
Sentiment Shifts
Once revered, SVB's reputation deteriorated swiftly online. By March 10, 2023, discussions turned intensely negative, highlighting the power and impact of public sentiment on financial institutions.
Emotions and Reactions
Despite government assurances, the dominant online emotion was anger. Many viewed the intervention as a bailout reminiscent of the 2008 Financial Crisis. Figures like Ben Bernanke faced significant backlash.
Lessons on Brand Trust
The SVB crisis underscores the fragile nature of financial trust in a socially connected world. Maintaining credibility and transparency is crucial to avoiding similar downfalls.
Share this
- April 2025 (2)
- March 2025 (1)
- February 2025 (4)
- January 2025 (1)
- December 2024 (2)
- November 2024 (2)
- October 2024 (4)
- September 2024 (2)
- August 2024 (2)
- July 2024 (2)
- June 2024 (2)
- May 2024 (2)
- April 2024 (2)
- March 2024 (2)
- February 2024 (2)
- January 2024 (2)
- December 2023 (3)
- November 2023 (4)
- October 2023 (4)
- September 2023 (4)
- August 2023 (4)
- July 2023 (4)
- June 2023 (3)
- May 2023 (5)
- April 2023 (3)
- March 2023 (6)
- February 2023 (3)
- January 2023 (4)
- December 2022 (2)
- November 2022 (3)
- October 2022 (4)
- September 2022 (2)
- August 2022 (3)



.png?width=64&height=64&name=linkedin%20(1).png)
